All About The Lydian - Mixed-Use Development - Confluence Companies

Meet 'World's Best' Lydian Nadaswaram at his debut concert in Chennai - The Hindu
The 10-Second Trick For The Lydian Scale - The Most Natural Mode - Music Interval

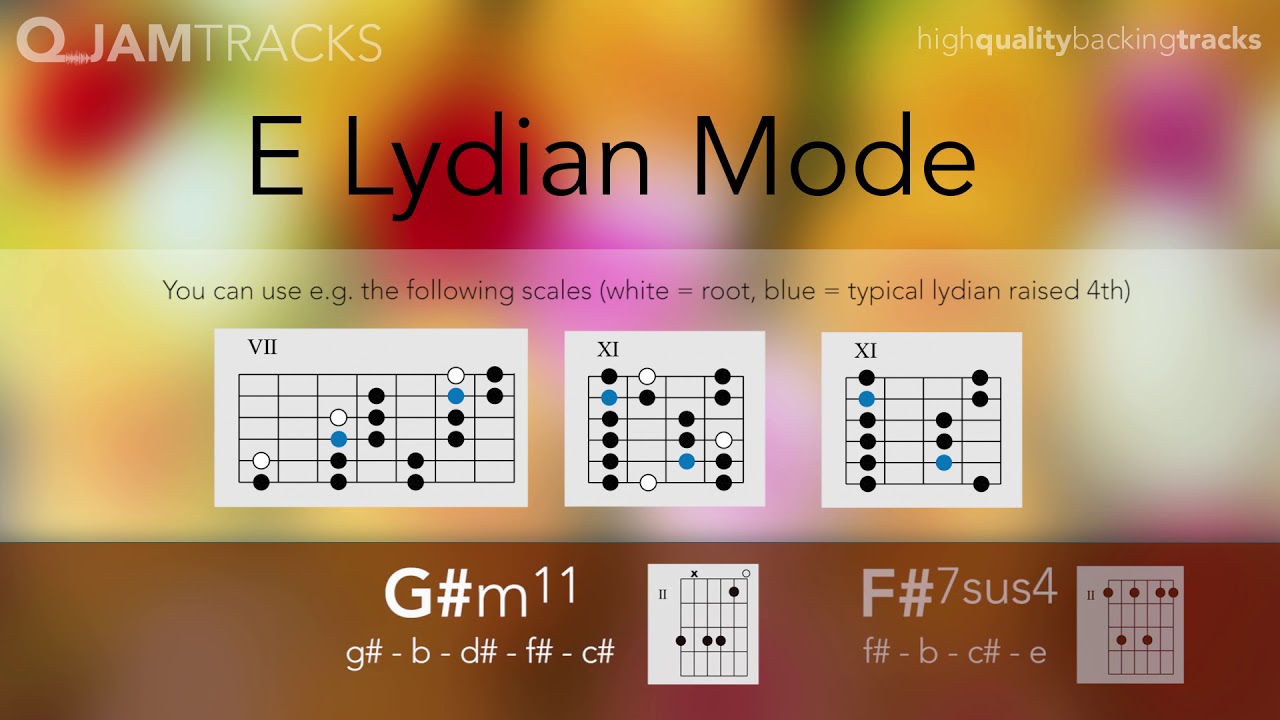
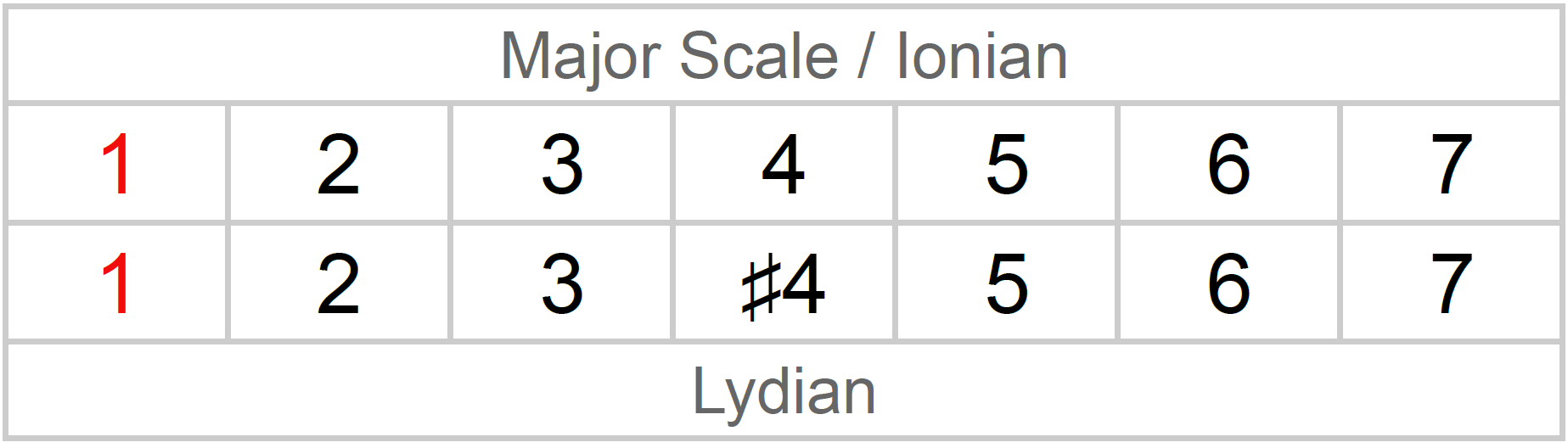
The modern Lydian mode is a seven-tone musical scale formed from an increasing pattern of pitches comprising 3 entire tones, a semitone, 2 more entire tones, and a last semitone. Since of the importance of the significant scale in modern-day music, the Lydian mode is typically referred to as the scale that begins on the fourth scale degree of the major scale, or alternatively, as the major scale with the fourth scale degree raised half an action.
The usage of the B instead of B would have made such piece in the modern-day day F significant scale. Ancient Greek Lydian [modify] The name Lydian describes the ancient kingdom of Lydia in Anatolia. In Greek music theory, there was a Lydian scale or "octave types" extending from parhypate hypaton to trite diezeugmenon, comparable in the diatonic genus to the modern-day Ionian mode (the major scale).
How to Play Lydian Mode on the Guitar - dummies
Middle ages Lydian mode [modify] In the Middle Ages and Renaissance, this mode was explained in two methods. The first way is the diatonic octave species from F approximately F an octave above, divided at C to produce two sections: The second is as a mode with a final on F and an ambitus extending to F an octave higher and in which the note C was considered as having an important melodic function.
The 6-Minute Rule for the LYDIAN CENTER – for INNOVATIVE HEALTHCARE
Modern Lydian mode [modify] The Lydian scale can be explained as a major scale with the fourth scale degree raised a semitone, making it an increased fourth above the tonic, e. g., an F-major scale with a B instead of B. This mode's increased 4th and the Locrian mode's decreased fifth are the only modes to have a tritone above the tonic.
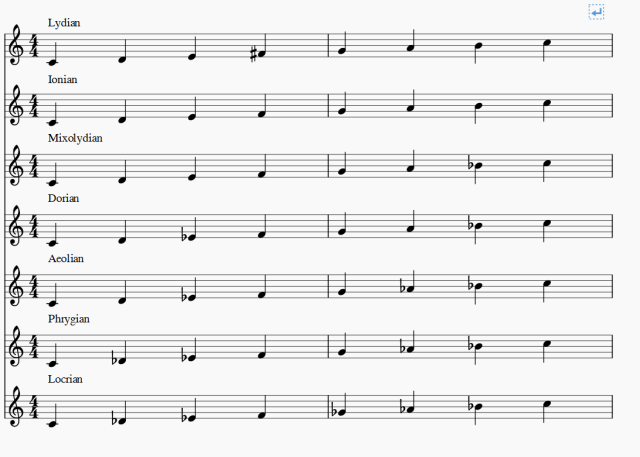

Lydian mode in all keys for treble clef
The subdominant is lessened. This Author developed on the remaining 3 scale degrees are small. Noteworthy structures in the Lydian mode [modify] Classical (Ancient Greek) [edit] The Paean and Prosodion to the God, familiarly referred to as the Second Delphic Hymn, composed in 128 BC by Athnaios Athenaou is predominantly in the Lydian tonos, both diatonic and chromatic, with areas likewise in Hypolydian.
